susan
You need 3 min read
Post on Feb 09, 2025
Table of Contents
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones: A Gardener's Essential Guide
Choosing the right plants for your garden is crucial for success. Knowing your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone is the first step to ensuring your plants thrive. This comprehensive guide will explain what USDA hardiness zones are, how to find yours, and why this information is vital for every gardener.
What are USDA Plant Hardiness Zones?
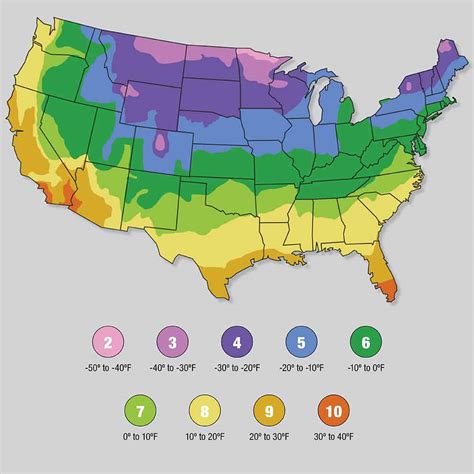
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides North America into 13 zones, each representing a range of average annual minimum winter temperatures. These zones are crucial because they indicate which plants are likely to survive the winter in a particular area. A plant's hardiness is determined by its ability to withstand the coldest temperatures it's likely to encounter.
Understanding the Zone Numbers: Each zone represents a 10° Fahrenheit (5.6° Celsius) range. For example, Zone 7a has an average annual minimum temperature between 0°F (-17.8°C) and 5°F (-15°C), while Zone 7b has an average annual minimum temperature between 5°F (-15°C) and 10°F (-12.2°C). The "a" and "b" subdivisions within each zone reflect subtle differences in minimum temperatures within that zone.
Why are Hardiness Zones Important?
Knowing your hardiness zone helps you:
- Choose the right plants: Selecting plants appropriate for your zone increases the chances of them surviving and thriving. Planting a plant outside its hardiness range can lead to winter damage or even death.
- Avoid costly mistakes: Investing in plants that won't survive your climate is a waste of time and money.
- Improve your gardening success: Understanding your zone allows you to plan your garden effectively, selecting plants that are well-suited to your local climate.
- Extend your growing season: By choosing plants appropriate for your microclimate (specific conditions in your yard), you can potentially extend the growing season.
Finding Your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone
The easiest way to find your zone is to use the interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. Simply enter your address to determine your specific zone.
Factors Affecting Microclimates: Remember that your specific location within a zone can have microclimates that affect plant hardiness. These microclimates are influenced by factors such as:
- Elevation: Higher elevations generally experience colder temperatures.
- Proximity to water: Bodies of water can moderate temperatures, creating warmer microclimates.
- Topography: Slopes and valleys can influence temperatures and drainage.
- Urban heat island effect: Cities tend to be warmer than surrounding rural areas.
Consider these factors when choosing plants for your garden, as they can affect the actual minimum temperatures your plants experience.
Beyond the Zones: Other Important Factors
While hardiness zones are a great starting point, they are not the only factor to consider when choosing plants. Other important factors include:
- Sunlight: Does your garden receive full sun, partial shade, or full shade?
- Soil type: Is your soil sandy, clay, loamy, or a combination?
- Moisture levels: Is your soil well-drained, moist, or wet?
- Pest and disease susceptibility: Certain plants are more susceptible to pests and diseases in particular areas.
By carefully considering all these factors, you can significantly improve your chances of creating a thriving and beautiful garden. Use the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map as a foundational guide, but remember to also account for the specifics of your unique garden environment.
Keywords: USDA Plant Hardiness Zones, Hardiness Zone Map, Plant Hardiness, Gardening, Gardening Tips, Choosing Plants, Microclimate, Average Minimum Temperature, Winter Temperatures, Garden Planning, Successful Gardening
Thanks for visiting this site! We hope you enjoyed this article.
